반응형
GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 방식의 URL 주소 설계
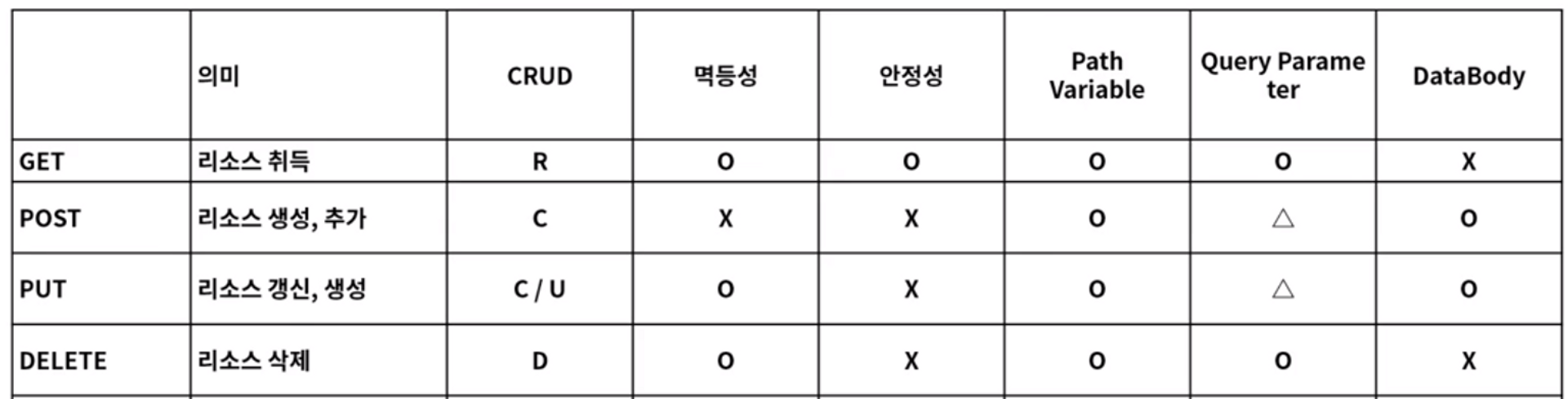
POST 방식 - C : create → insert / GET 방식 - R : read → select / PUT방식 - U : update / DELETE 방식 - D : delete
GET 방식
→ @RequestParam : 쿼리 파라미터 방식으로 값을 받는 방법
→ key = value 구조로 데이터 파싱 처리
→ Map 사용 방식 구조 처리
→ Dto 객체를 만들어서 처리 (@RequestParam을 붙이지 말아야 한다.)
→ @PathVariable 방식
GetApiController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 | @RestController @RequestMapping("/api") public class GetApiController { // http://localhost:8080/api/hello @GetMapping("/hello") public String getHello() { return "say hello"; } // 쿼리 파라미터 방식 // http://localhost:8080/api/queryParam1?name=짱구 @GetMapping("/queryParam1") public String queryParam1(@RequestParam String name) { return "name : " + name; } // key = value 방식 // 쿼리 스트링 방식으로 주소 설계를 했다면 요청시에 매개변수를 다 받아야 한다. // 아니면 오류 발생 (하지만 선택적 요소로 만들 수도 있다!) // 선택적 요소로 만들기 @RequestParam(required = false, deafultValue = "0")을 붙여준다. // http://localhost:8080/api/queryParam2?name=짱구 // http://localhost:8080/api/queryParam2?name=짱구&age=5 @GetMapping("/queryParam2") public String queryPara2(@RequestParam String name , @RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "0") int age) { System.out.println("name : " + name); System.out.println("age : " + age); return "name, age : " + name; } // Map 방식 // 약속 지켜 하나하나 매개변수를 다 넣지 않더라도 실행됨. // http://localhost:8080/api/queryParam3?name=홍&age=3 @GetMapping("/queryParam3") public String queryParam3(@RequestParam Map<String, String> data) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); data.entrySet().forEach({ System.out.println(entry.getKey()); System.out.println(entry.getValue()); System.out.println(); sb.append(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue()); }); System.out.println("data : " + data.toString()); return "파싱 - map 방식의 이해 : " + sb.toString(); } // DTO 객체 만들어서 처리 // !!!!! RequestParam을 붙이지 말아야 한다 !!!!! // http://localhost:8080/api/queryParam4?name=홍&age=3 @GetMapping("/queryParam4") public String queryParam4(UserRequest userDto) { System.out.println("Dto 방식 동작 처리"); System.out.println(userDto.getName()); System.out.println(userDto.getAge()); System.out.println(userDto.getEmail()); return userDto.toString(); } // @PathVariable 방식 // http://localhost:8080/api/path-variable/10 @GetMapping("/path-variable/{userId}") public String pathVariable1(@PathVariable int userId) { System.out.println("userId : " + userId); return "userId" + userId; } // http://localhost:8080/api/users/1/orders/1 @GetMapping("/users/{userId}/orders/{orderId}") public String getOrder(@PathVariable int userId, @PathVariable int orderId) { return "userId : " + userId + ", orderId : " + orderId; } // http://localhost:8080/api/name/하이/age/3 // !!!!! @PathVariable을 붙이지 말아야 한다 !!!! @GetMapping("/name/{name}/age/{age}") public UserRequest getUser(UserRequest dto) { UserRequest userRequest = new UserRequest(); userRequest.setName(dto.getName()); userRequest.setAge(dto.getAge()); return userRequest; } } | cs |
UserRequest.java (UserDTO)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | package com.example.demo.model; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.ToString; @Getter @Setter @ToString public class UserRequest { private String name; private int age; private String email; } | cs |
POST 방식
→ @RequestBody
→ DTO 방식
→ @JsonProperty(”phone_number”) : 스네이크케이스와 카멜케이스를 구분하여 파싱 해줌.
PostApiController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | @RestController @RequestMapping("/api2") public class PostApiController { // http://localhost:8080/api2/post1/reqData @PostMapping("/post1") public void post1(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> reqData) { reqData.entrySet().forEach(e -> { System.out.println("key : " + e.getKey()); System.out.println("value : " + e.getValue()); }); } // http://localhost:8080/api2/post2 @PostMapping("/post2") public PostReqDto post2(@RequestBody PostReqDto reqDto) { return reqDto; } } | cs |
PostReqDto.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | package com.example.demo.model; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.ToString; @Getter @Setter @ToString @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class PostReqDto { private String name; private String email; private int age; private int hobby; // 코드 컨벤션이 깨지지 않도록 방지 // name이 phone_number일 경우 phoneNumber로 파싱되어 데이터가 들어감. @JsonProperty("phone_number") private int phoneNumber; } | cs |
PUT 방식
→ @PutMapping
→ Dto 안에 List<Object> 타입 만들어보기
→ JSON 배열 형식에 이해
→ @JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategies.SnakeCaseStrategy.class)
: 자동으로 스네이크 케이스로 바꿔줘서 파싱됨.
PutApiController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | @RestController @RequestMapping("/api") public class PutApiController { // http://localhost:8080/api/put1 @PutMapping("/put1") public PostRequestDto put(@RequestBody PostRequestDto req) { System.out.println("req : " + req); return req; } // http://localhost:8080/api/put2 @PutMapping("put2") public PutRequestDto put2(@RequestBody PutRequestDto reqDto) { System.out.println("reqDto : " + reqDto); return reqDto; } } | cs |
CarDTO.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | package com.example.demo2.model; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.PropertyNamingStrategies; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonNaming; import lombok.Data; @Data // 자동으로 스네이크 케이스로 바꿔줘서 파싱됨. @JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategies.SnakeCaseStrategy.class) public class CarDTO { private String name; private String carNumber; } | cs |
PutRequestDto.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | package com.example.demo2.model; import java.util.List; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.PropertyNamingStrategies; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonNaming; import lombok.Data; @Data @JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategies.SnakeCaseStrategy.class) public class PutRequestDto { private String name; private String age; private List<CarDTO> carList; } | cs |
DELETE 방식
→ @DeleteMapping
→ @PathVariable
→ @RequestParam
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | @RestController @RequestMapping("/api2") public class DeleteApiController { // http://localhost:8080/api2/delete/{userId}?account=이름 // http://localhost:8080/api2/delete/asdf?account=우리은행 @DeleteMapping("/delete/{userId}") public void delete(@PathVariable String userId, @RequestParam String account) { System.out.println("userId : " + userId); System.out.println("account : " + account); } } | cs |
반응형
'프로그래밍 > Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Boot_어노테이션 (0) | 2023.04.13 |
|---|---|
| Spring Boot_AOP 관점 지향 프로그래밍 (0) | 2023.04.13 |
| Spring Boot_제어의 역전과 의존 주입 (IoC/DI) (0) | 2023.04.13 |
| Spring Boot_Response와 MIME TYPE에 이해와 ResponseEntity (0) | 2023.04.13 |
| Spring Boot_도구 설치 및 환경 설정 (0) | 2023.04.09 |



