DBHelper 클래스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 | package com.tenco.myblog.utils; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * * mysql 서버와 연결을 해주는 객체 * * Connection 객체를 생성하고 반환하는 처리 1DBHelper */ public class DBHelper { private static final String DB_HOST = "localhost"; private static final String DB_PORT = "3306"; private static final String DB_DATABASE_NAME = "myblog"; private static final String DB_CHARSET = "UTF-8"; private static final String DB_USER_NAME = "bloguser"; private static final String DB_PASSWORD = "1q2w3e4r5t"; private Connection conn; // 싱글톤 패턴 // 1. 기본 생성자를 만들어서 private으로 설정 private DBHelper() { } // 2. 자기 자신을 private으로 선언 (외부에서 접근하지 못하도록) private static DBHelper dbHelper; // 3. 외부 어디서든지 접근 가능한 static 메서드를 만들어준다. (메서드) public static DBHelper getInstance() { if (dbHelper == null) { dbHelper = new DBHelper(); } return dbHelper; } public Connection getConnection() { if (conn == null) { // 한번도 생성하지 않았다면 동작 String urlFormat = "jdbc:mysql://%s:%s/%s?serverTimezone=Asia/Seoul&characterEncoding=%s"; String url = String.format(urlFormat, DB_HOST, DB_PORT, DB_DATABASE_NAME, DB_CHARSET); try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, DB_USER_NAME, DB_PASSWORD); System.out.println(">> DB 연결 완료 <<"); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(">> DBHelper 에서 오류가 발생 했어! <<"); e.printStackTrace(); } } return conn; } public void closeConnection() { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } conn = null; } } | cs |
→ DB에 있는 부분을 연동하려면 Connection 객체가 필요하다.
주소, 포트 번호, 데이터베이스 이름, 사용할 문자셋, 계정, 비번으로 접근하여 활용 가능한 부분들을 Connection이라는 객체에 저장한다.
IBlogDAO인터페이스 (select, delete)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | package com.tenco.myblog.dao; import com.tenco.myblog.dto.BlogDTO; // public abstract 생략 public interface IBlogDAO { void select(); // 전체 조회 BlogDTO select(int id); // id 기반으로 조회 int delete(int boardId); // boardId 기반으로 삭제 } | cs |
→ 인터페이스에서 만들고자 하는 기능의 틀을 만들어 UserDAO에서 구현한다.
BlogDTO 클래스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 | package com.tenco.myblog.dto; public class BlogDTO { private int id; private String title; private String content; private int readCount; private int userId; public BlogDTO() { } public BlogDTO(String title, String content, int userId) { this.title = title; this.content = content; this.userId = userId; } @Override public String toString() { return "BlogDTO [id=" + id + ", title=" + title + ", content=" + content + ", readCount=" + readCount + ", userId=" + userId + "]"; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; } public int getReadCount() { return readCount; } public void setReadCount(int readCount) { this.readCount = readCount; } public int getUserId() { return userId; } public void setUserId(int userId) { this.userId = userId; } } | cs |
→ 데이터베이스의 데이터에 접근하여 데이터를 가져오기 위해 데이터들을 멤버 변수로 생성하고 get, set 메서드를 만든다.
BlogDAO 클래스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 | package com.tenco.myblog.dao; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import com.tenco.myblog.dto.BlogDTO; import com.tenco.myblog.utils.DBHelper; public class BlogDAO implements IBlogDAO { private Connection conn; private PreparedStatement pstmt; private ResultSet rs; public BlogDAO() { conn = DBHelper.getInstance().getConnection(); } @Override public void select() { } // 2차원 표를 클래스로 모델링 하기 위해 DTO 만들기 @Override public BlogDTO select(int id) { BlogDTO blogDTO = null; String query = " SELECT * " + " FROM board " + " WHERE id = ? "; try { pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(query); pstmt.setInt(1, id); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); // blogDTO에 결과값을 담음 while (rs.next()) { blogDTO = new BlogDTO(); blogDTO.setId(rs.getInt("id")); blogDTO.setTitle(rs.getString("title")); blogDTO.setContent(rs.getString("content")); blogDTO.setReadCount(rs.getInt("readCount")); blogDTO.setUserId(rs.getInt("userId")); } } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println(">> BlogDAO select(int id) 에러 발생 <<"); e.printStackTrace(); } return blogDTO; } @Override public int delete(int boardId) { int resultRow = 0; String sql = " DELETE FROM board " + " WHERE id = ? "; try { pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setInt(1, boardId); // 반환타입이 int이므로 resultRow를 받음 resultRow = pstmt.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println(">> delete 에러 발생 <<"); e.printStackTrace(); } return resultRow; } } | cs |
→ IUserDAO 인터페이스를 구현하여 메서드를 구현한다.
→ BlogDTO select(int id) 메서드
: id 기반으로 조회하기 때문에 매개변수에 int id를 넣어 main에서 사용할 수 있게 한다.
: select()는 쿼리문을 실행하면 2차원 표를 클래스로 모델링 하기 때문에 DTO를 반환타입으로 받고 .executeQuery();를 사용해야 한다.
: blogDTO의 결과값을 담기 위해 while()문을 사용해야 한다.
→ int delete(int boardId) 메서드
: boardId 기반으로 조회하기 때문에 매개변수에 int boardId를 넣어 main에서 사용할 수 있게 한다.
: select() 제외 delete(), save(), create()는 전부 반환 타입으로 int값을 받고 .executeUpdate();를 사용해야 한다.
BlogService 클래스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | package com.tenco.myblog.service; import com.tenco.myblog.dao.BlogDAO; import com.tenco.myblog.dto.BlogDTO; // 입력한 값의 형식을 확인, DAO를 이용해서 활용하는 ..! public class BlogService { private BlogDAO blogDAO; public BlogService() { blogDAO = new BlogDAO(); } // 하나의 게시글 찾는 로직 만들기 public BlogDTO selectByBoardId(int id) { BlogDTO resultDTO = blogDAO.select(id); return resultDTO; } public int deleteBoardById(int boardId, int userId) { int resultRow = 0; // 검증 : userId 값과 blogWriterId // board 테이블에 있는 작성자의 userId 값이 같은지 확인 BlogDTO blogDTO = selectByBoardId(boardId); //blogDto null일 때 방어적 코드 작성 if (blogDTO != null) { int blogWriterId = blogDTO.getUserId(); // 같은 사람이다. 를 인증하기 위한 if문 if (blogWriterId == userId) { // 삭제 요청 처리 resultRow = blogDAO.delete(boardId); } } return resultRow; } } | cs |
→ 입력한 값의 형식을 확인하고 DAO를 이용해서 활용하는 메서드를 만든다.
→ BlogDAO클래스 객체를 생성하여 select()를 사용할 수 있게 한다.
→ BlogDTO selectByBoardId(int id) 메서드
: 하나의 게시글을 찾는 로직
→ int deleteBoardById(int boardId, int userId) 메서드
: 작성자와 userId값이 같아야 글을 삭제할 수 있으므로 userId값과 blogWriterId가 같은지 확인하고 같은 사람이면 삭제 요청을 처리한다.
BlogController 클래스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | package com.tenco.myblog.controller; import com.tenco.myblog.dto.BlogDTO; import com.tenco.myblog.service.BlogService; // (main에서) 외부에서 오는 요청을 담당한다. public class BlogController { private BlogService blogService; public BlogController() { blogService = new BlogService(); } public BlogDTO requestBoardContentById(int id) { BlogDTO responseDTO = blogService.selectByBoardId(id); return responseDTO; } // 하나의 게시글 삭제하기 main -> controller -> Service -> DAO public int requestDeleteBoardById(int boardId, int userId) { int responseRow = blogService.deleteBoardById(boardId, userId); return responseRow; } } | cs |
→ main에서 오는 요청을 담당한다.
→ BlogService 객체를 생성하여 selectByBoardId()와 deleteBoardById를 사용하여 요청을 담당한다.
MainTest
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | package com.tenco.myblog; import com.tenco.myblog.controller.BlogController; import com.tenco.myblog.dto.BlogDTO; public class MainTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // select(int id) 코드 테스트 BlogController blogController = new BlogController(); BlogDTO dto = blogController.requestBoardContentById(4); System.out.println(dto); // delete(int boardId, int userId) 코드 테스트 int result = blogController.requestDeleteBoardById(30, 3); System.out.println(result); } // end of main } | cs |
요청 순서
main → Controller → Service → Dao → Mysql
요청 후 응답
main ← Controller ← Service ← Dao ← Mysql
<결과 화면>
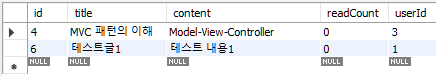
select(int id) 코드 테스트

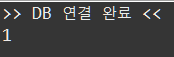
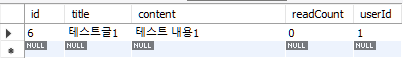
delete(int boardId, int userId) 코드 테스트
'프로그래밍 > Database' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Oracle_MERGE INTO 문 (0) | 2023.09.06 |
|---|---|
| Oracle_WHERE 1=1 (0) | 2023.08.29 |
| MySQL_GROUP BY절 (0) | 2023.03.10 |
| MySQL_N : M 관계 (0) | 2023.03.10 |
| MySQL_MySQL FUNCTION (0) | 2023.03.10 |

